EN 13501-1 Fire Test for Building Materials
EU Construction Products Regulation
The EU Construction Products Regulation (CPR) is the basis of the construction products regulation used by all EU member states. The CPR requires member states to reclassify all construction products using a new common test method. These products include all wall linings, flooring and other fixed products such as linear pipe, insulation products, and cables.
The CPR requires all member states to amend their regulations to incorporate the classification system described in EN 13501 and to use the test methods referenced therein.
The classification criteria and test methods used to assess the performance of products covered by the CPR in terms of their reaction to fire are EN 13501-1 Fire classification of construction products and building elements – Part 1: Classification using data from reaction to fire tests.
EN 13501-1 is to define a standardized procedure for the classification of reaction to fire for all construction products, including products incorporated within building elements. The following 5 EN/ISO test methods are used in the EN 13501-1:
Test method/standards involved in EN 13501-1
| EN 13823 | Reaction to fire tests for building products — Building products excluding floorings exposed to the thermal attack by a single burning item. |
| EN ISO 1182 | Reaction to fire tests for building products — Non-combustibility test. |
| EN ISO 1716 | Reaction to fire tests for building products — Determination of the gross heat of combustion (calorific value). |
| EN ISO 9239-1 | Reaction to fire tests for floorings — Part 1: Determination of the burning behavior using a radiant heat source. |
| EN ISO 11925-2 | Reaction to fire tests — Ignitability of building products subjected to direct impingement of flame — Part 2: Single-flame source test. |
The EN 13501-1 classification system for reaction to fire performance of construction materials is now also widely used outside the EU, both by countries and manufacturers wishing to trade with Europe for these products and by countries wishing to establish or upgrade their own regulations without spending large R&D costs.
EN 13501-1 Classification & Performance Criteria
Construction products are treated as three separate categories in EN 13501-1:
Construction products, excluding floorings and linear pipe thermal insulation products;
Floorings;
Linear pipe thermal insulation products.
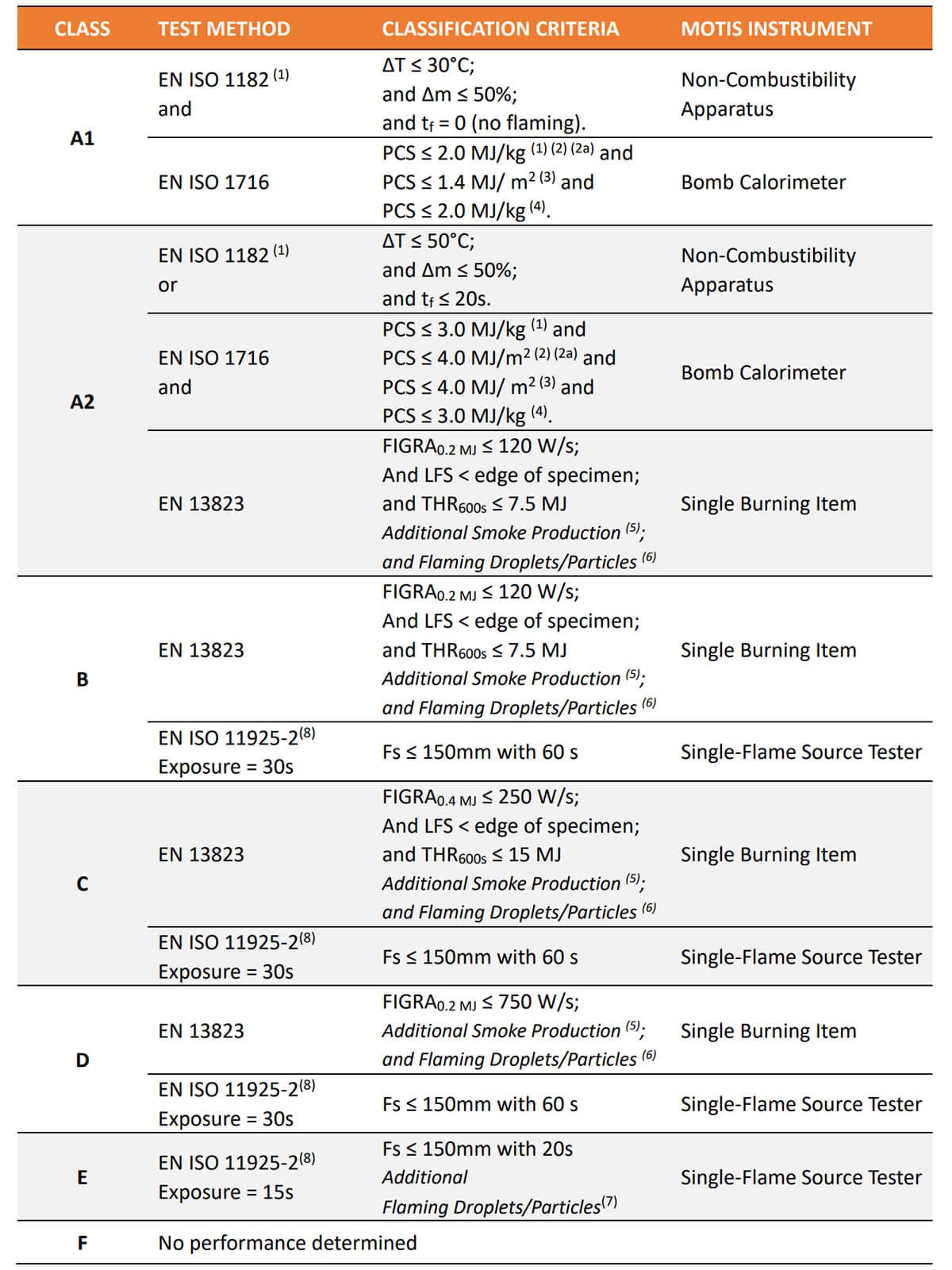
Each of these product categories has 5 performance classes A1, A2, B, C, D, and E and a non-performance determined 'F' class, as well as criteria and test methods for assessing the performance of products in reaction to fire.
The classification & performance criteria of all building materials are separated into 3 tables:
Table 1 EN 13501-1 Class of Reaction to Fire Performance for Construction Products excluding Floorings & Linear Pipe Thermal Insulation Products
Table 2 EN 13501-1 Class of Reaction to Fire Performance for Floorings
Table 3 EN 13501-1 Class of Reaction to Fire Performance for Linear Pipe Thermal Insulation Products
The test specimen in φ 45mm by 50mm height is inserted into a stabilized furnace at 750 degrees, and the temperature of the furnace, surface, and center of the specimen will be measured. In the meantime, the flaming time, and mass loss of the specimen are measured during the test.
Test Procedure of the Non-Combustibility Test
a) Prepare 5 sets of test specimens (conditioning and weight).
b) Stabilize the furnace at a temperature of 750 degrees. The temperature drift should not be more than 2 degrees. The maximum deviation of the average temperature should not be more than 10 degrees in the last 10min.
c) Install one specimen into the specimen holder.
d) Insert the specimen holder in the furnace.
e) Start the operation software running immediately following the insertion of the specimen.
f) Carry out the test for a period of 30min.
g) Record the burning behavior during the test, and the temperature rise (auto record by the software).
h) Stop the test if the temperature equilibrium (drift does not exceed 2 degrees at the last 10min), or continue the test up to 60min.
i) Remove the specimen holder and cool down in a desiccator, weigh the specimen and calculate the mass loss.
j) Test all five specimens with the same procedure.
Key Test Results:
Mass Loss, in percentage.
Sustained flaming time, in seconds.
Temperature rise, in degrees.
A specimen in specified mass is burned under standardized conditions, at constant volume, in an atmosphere of oxygen, in a bomb calorimeter calibrated by combustion of certified benzoic acid. The heat of combustion determined under these conditions is calculated on the basis of the observed temperature rise, taking account of heat loss and the latent heat of vaporization of water.
Test Procedure of the Bomb Calorimeter Test
a) Prepare 3 sets of test specimens (sampling & conditioning)
b) Weight a specimen and place it in the crucible.
c) Place the crucible in the holder, attach the firing wire and loop it to touch the specimen (10ml de-ionized water is added to the calorimetric bomb to absorb the combustion gases).
d) Place the holder in the calorimetric bomb, and tighten the lid.
e) Fill the oxygen into the calorimetric bomb until a pressure of 3.0 to 3.5 MPa is achieved.
f) Insert the bomb in the calorimetric vessel.
g) Introduce the calorimeter system into ready condition.
h) Start the test with the auto program of the calorimeter system.
i) Check the test result.
j) Remove the bomb from the calorimeter vessel.
k) Cooling down and slowly reducing the pressure. Open the bomb and clean the combustion residues.
l) Test all three specimens with the same procedure.
Key Test Results:
Gross heat of combustion, in MJ/kg.
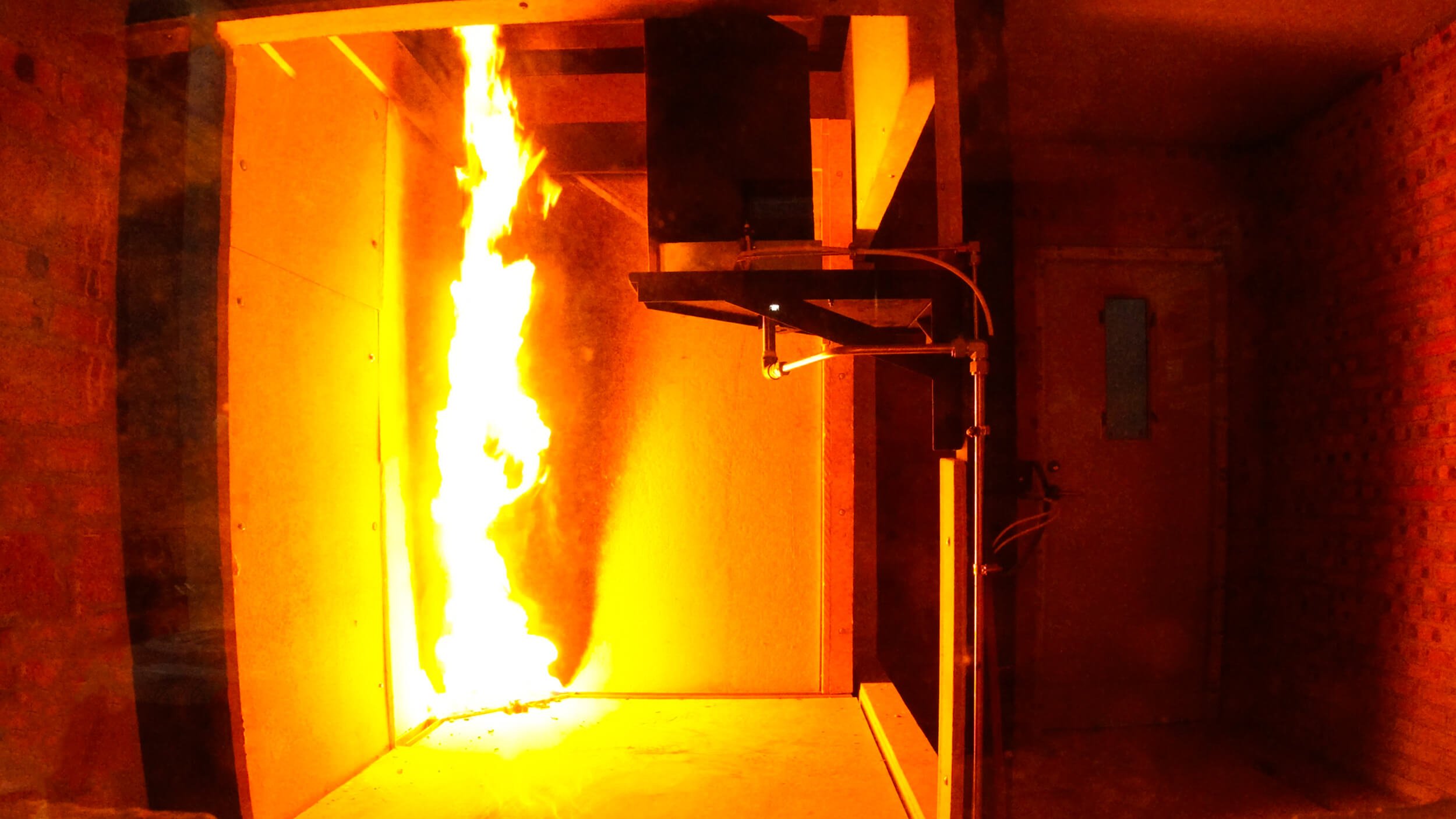
A specimen is placed in the corner of the trolley and the trolley is positioned underneath the exhaust system. The sample is exposed to a propane-fueled sandbox ignition source (30.7kw), the combustion gases are collected by the exhaust hood and duct, and the calorimeter system will sample gases and calculate the heat release (THR600), smoke production (TSP600s), FIGRA 0.2MJ, and SMOGRA results. In the meantime, the specimen reaction to fire behavior is visible by the side observation window.
Test Procedure of the SBI Test
a) Prepare 3 sets of test specimens (conditioning).
b) Install the specimens in the trolley and push the trolley into the test room.
c) Set up the test system, including volume flow of the exhaust (0.6 cube meter per second), heat release measurement system (temperature, duct flow, oxygen and carbon monoxide analyzer).
d) Start the standard test procedure, the test will be conducted as per the following test program.
d.1) The pilot flames are ignited.
d.2) At time = 120s, the secondary burner is ignited, output the 30.7kw propane-flued ignition source.
d.3) At time = 300s, the propane supply is switched to the primary burner from the secondary burner.
d.4) At time = 1560s, the propane supply is terminated.
e) Observe the burner behavior of the specimen during the test.
f) Export the test results from the heat release measurement system.
g) Test all three sets of specimens with the same procedure.
Key Test Results:
Heat release rate, HRR, in kW.
Total heat release, THR, MJ.
Fire growth rate indices, FIGRA, W/s.
Smoke production rate, SPR, in m2/s.
Total smoke production, TSP, in m2.
Smoke growth rate index, SMOGRA, in cm2/s2.
Lateral flame spread.
Flaming particles or droplets.
A specimen is placed in a horizontal position below a gas-flued radiant panel inclined at 30° where it is exposed to a defined heat flux. A pilot flame is applied to the hotter end of the specimen. During the test, any flame front which develops is noted and a record is made of the progression of the flame front horizontally along the length of the specimen in terms of the time it takes to spread to defined distances. Also, the smoke development during the test is recorded as the light transmission in the exhaust stack.
Test Procedure of the Flooring Radiant Panel Test
a) Prepare 3 sets of test specimens (conditioning).
b) Install the specimens to the specimen holder.
c) Set up the test system, including airflow (2.5m/s) in the exhaust stack, chamber temperature stabilization, smoke-measuring system.
d) Ignite the pilot burner.
e) Put the specimen holder on the sliding platform of the test chamber, and slide it into the chamber.
f) Start the test.
g) Record the flame spread distance and burning behavior during the radiant panel test.
h) Terminate the test after 30min. Remove the specimen and export the test result from the software.
i) Test all three sets of specimens with the same procedure.
Key Test Results:
Critical heat flux, CHF, in kW/m2.
Flame spread distance, in mm.
The integral of smoke obscuration, in % x min.
A specimen is mounted vertically and exposed to a small flame (20mm height), the ignition time (after the small flame removal), flame spread height, and presence of droplet/particles is recorded during the single-flame source test.
Test Procedure of the Single-Flame Source Test
a) Prepare 6 sets of test specimens, three lengthwise and three crosswise (conditioning).
b) Check the required airflow velocity (0.7 m/s) in the chimney of the combustion chamber.
c) Install the specimen to the specimen holder and mount the holder into the test chamber.
d) Light the burner and adjust the flame height to 20mm in the vertical direction.
e) Tilt the burner to 45 degrees.
f) Impingement of the flame to the specimen (surface or edge exposure) 15 seconds.
g) Remove the flame after 15 seconds, and record the flaming time, flame spread height, and droplets during the test.
h) Test all six sets of specimens with the same procedure.
Key Test Results:
Ignition time, in second.
Whether or not the flame tip reaches 150mm above the flame application point.
Presence of droplets/particles.
Summary
EN 13501-1 is a reaction to fire classification procedure for all construction products & building elements. Construction products used in European must follow EN 13501-1 to achieve classification according to their end use application.
EN 13501-1 separates all types of products into three categories, which are: construction products, floorings, and linear insulation products. These products have to be tested in 4 of 5 test methods to determine performance in classes A to F.
Furthermore, EN 13501-1 has become a building regulation or published as an equivalent standard in other countries outside European. It helps these countries establish their fire regulation quickly & low cost, also manufacturers could sell without additional R&D and re-class.
Contents NAV
EU Construction Products Regulation
EN 13501-1 Class and Performance
EN 13501-1 Test Methods Introduction
01 Non-Combustibility Test
02 Bomb Calorimeter
03 Single Burning Item
04 Flooring Radiant Panel
05 Single-Flame Source Test
Summary
Link to Instruments
ISO 1182 Non-Combustibility Apparatus
ISO 1716 Bomb Calorimeter
EN 13823 Single Burning Item
ISO 9239-1 Flooring Radiant Panel
ISO 11925-2 Single-Flame Source Tester