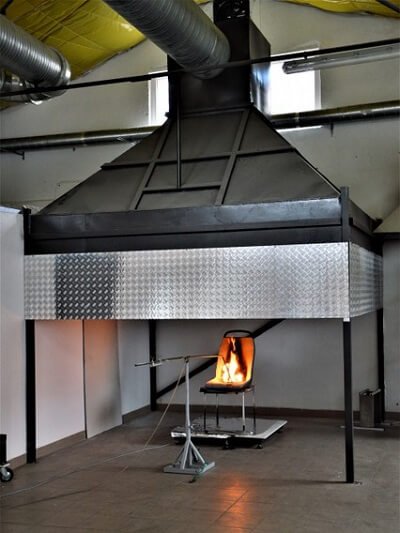

EN 16989 Explanation | Railway Vehicle Seat Fire Test
EN 16989 is a test protocol to determine the burning behaviour of a rail vehicle seat design using a set of complete seats exposed to a 15kw open flame under an exhaust hood. It also sets out a standardized procedure to assess a seat’s potential for vandalization. EN 16989 is referred to as a standard test method in EN 45545-2 to assess the performance of vehicle seats used in railway vehicles.
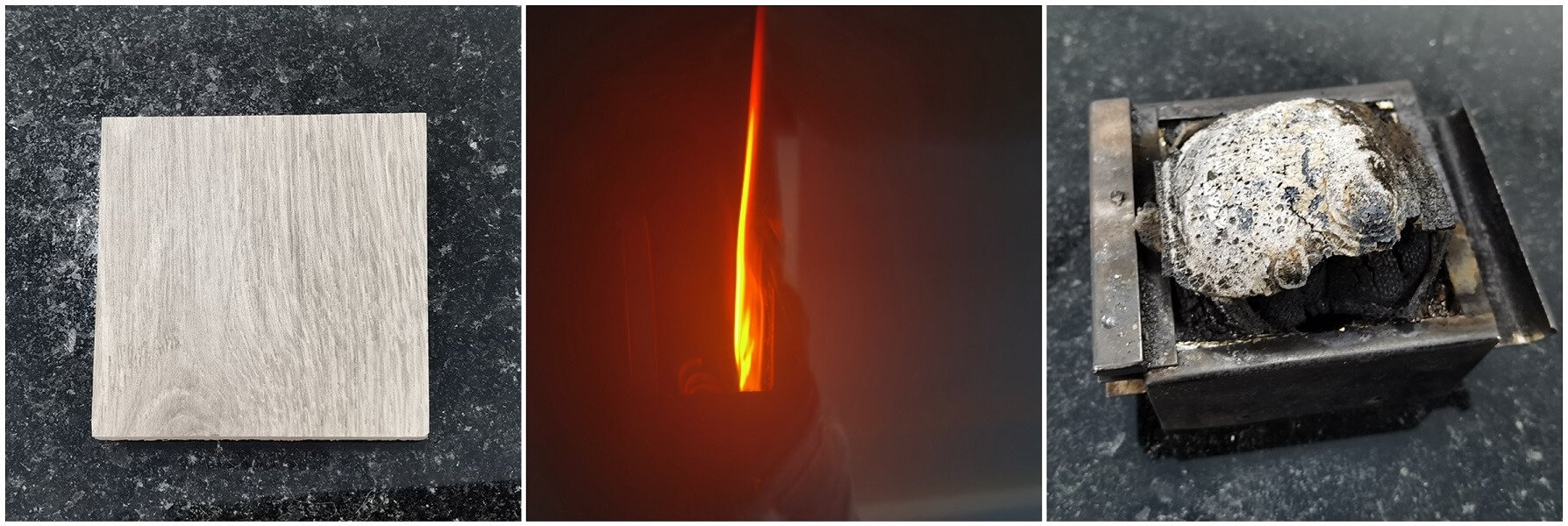

Smoke Density Test: ISO 5659 VS ASTM E662
ISO 5659-2 and ASTM E662 are used to measure the smoke density generated from burning materials. Both test methods use the same test chamber and photometric system.
The most obvious difference between the two is that use different kinds of radiant heat sources. It leads to different test results which are not comparative.
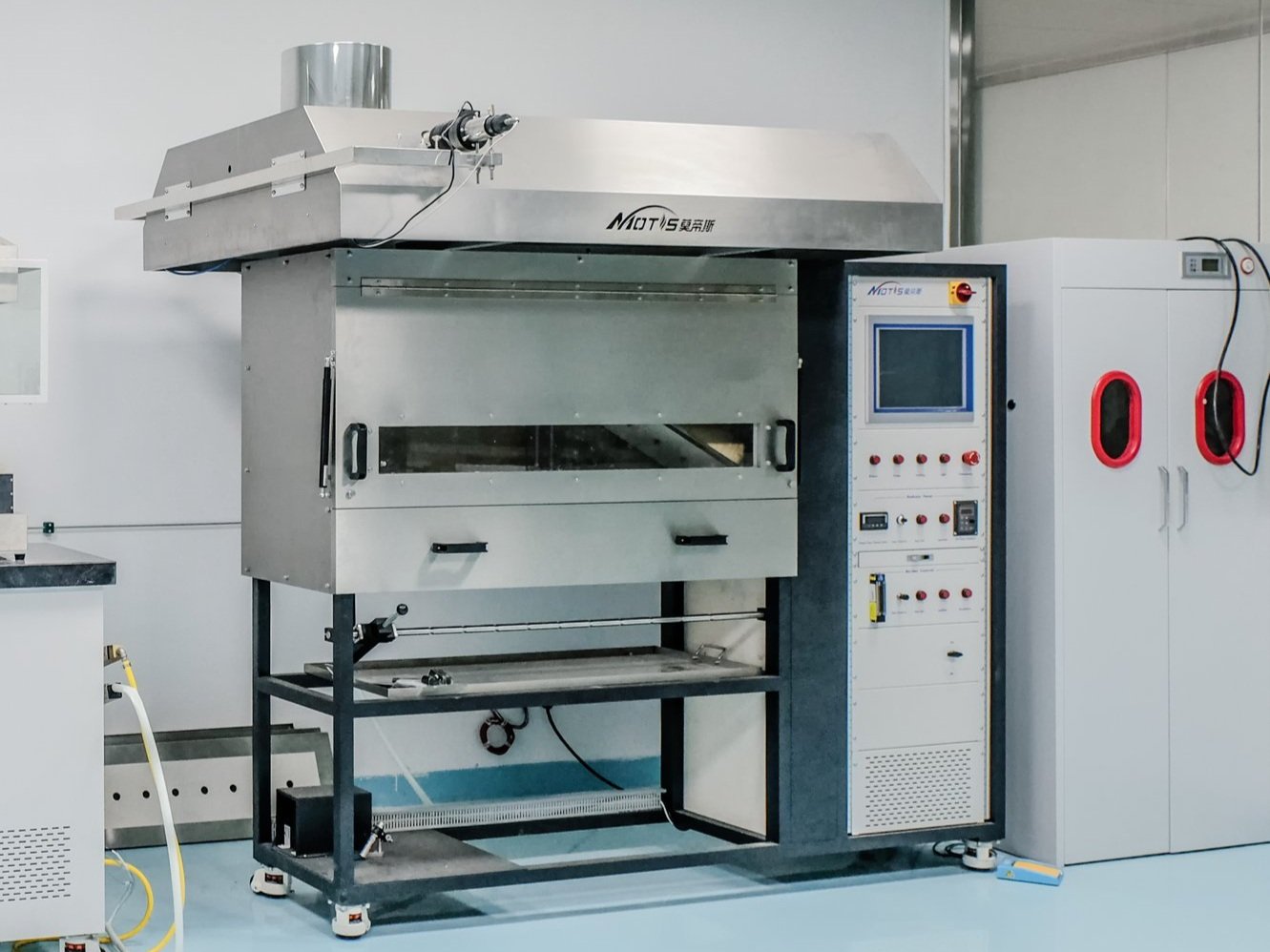

Annual Maintenance for Flooring Radiant Panel
The Flooring Radiant Panel is used for determining the critical radiant flux of horizontally-mounted floor covering systems, which are exposed to a flaming ignition source in a specific radiant heat environment. The equipment is widely used in different area standards. Annual maintenance ensures that the instrument is always in good working condition.
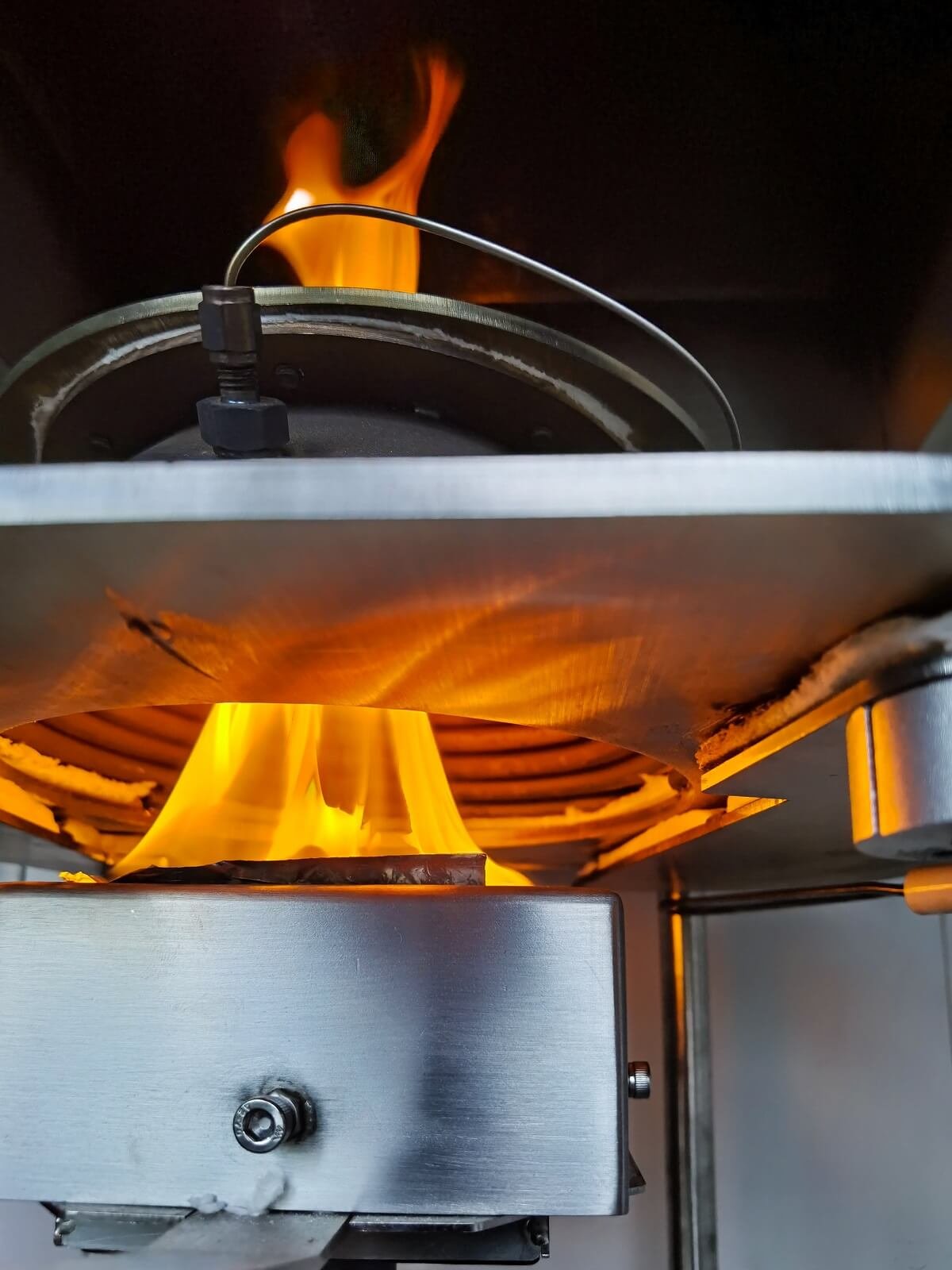

What is the Cone Calorimeter Test?
The Cone Calorimeter offers a method for assessing the heat release rate and dynamic smoke production rate of specimens exposed to specified controlled irradiance levels with an external igniter. It is a critical instrument in fire testing and research that are more repeatable, more reproducible, and easier to conduct.

Battery Cell Safety Concerns: Thermal Runaway.
The lithium-ion batteries have become pervasive in almost every aspect of our daily lives, and are also known to pose a number of significant safety risks if not handled properly. The study of the thermal runaway of battery cells is important for safety research.
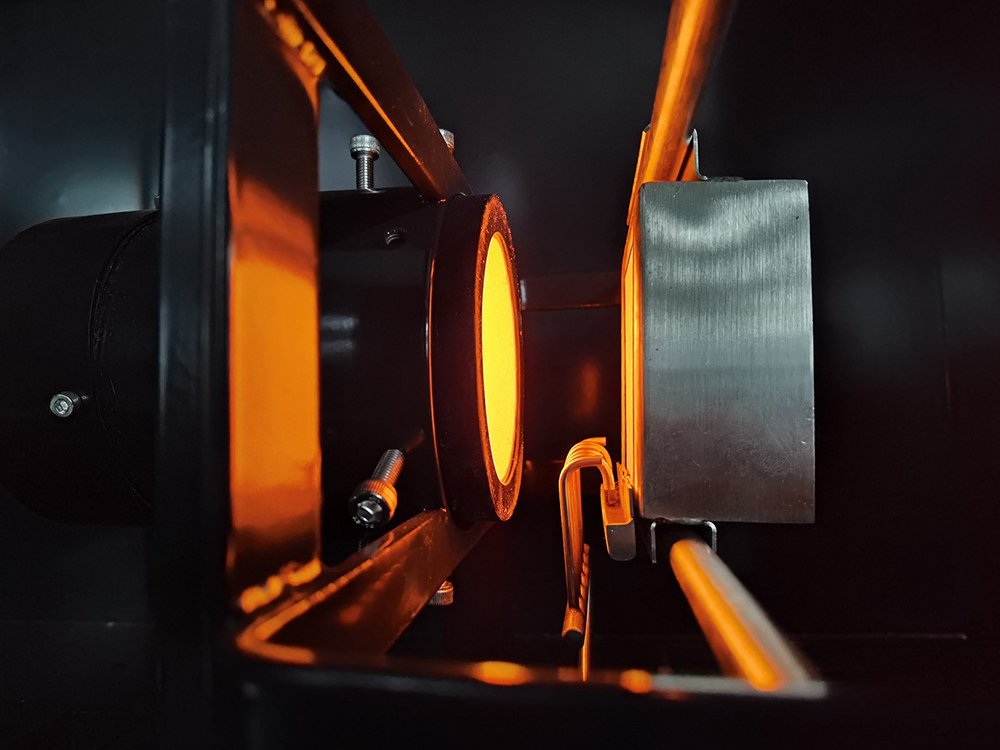
What is the NBS Smoke Density Chamber?
The NBS Smoke Density Chamber measures the specific optical density of smoke generated by the materials using an essentially flat specimen (up to 25 mm thick) exposed to a specific radiant heat source (normally 25 or 50 kW/m2), in a closed chamber, with or without a pilot flame.
